What Rm Process Step Requires a Cycle of Continuous Reassessment
Advertisements
A Hazard Management Plan (RMP) is prepared past a projection manager to address risks, their potential bear on on a program and consists of ways to reduce these risks. The RMP tells the government and contractor team how they plan on reducing risks to a certain level by a certain time.
Advertisements
Definition:
A take chances management programme is a detailed document that explains an organization's risk management procedure.
Agreement Chance Direction
Chance direction is a continuous process that is accomplished throughout the life cycle of a organisation and should begin at the earliest stages of programme planning. Information technology is an organized methodology for continuously identifying and measuring the unknowns; developing mitigation options; selecting, planning, and implementing appropriate risk mitigations; and tracking the implementation to ensure successful risk reduction. Effective gamble management depends on chance management planning; early on identification and analyses of risks; early implementation of corrective actions; continuous monitoring and reassessment; and communication, documentation, and coordination. It's most effective if it is fully integrated with the program's Systems Engineering, Program Management, and Exam & Evaluation processes.
Advertisements
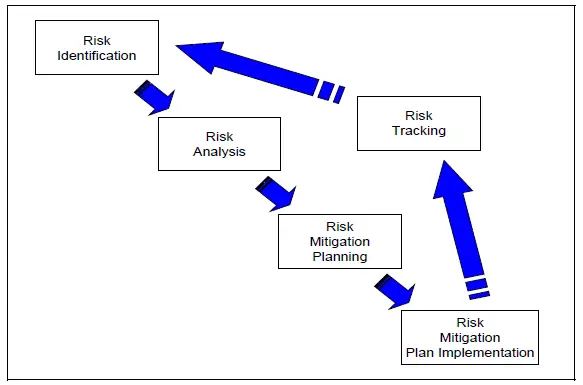
Take a chance Management Plan (RMP) Topics
The run a risk management plan should address the following continuous cardinal activities as shown higher up:
- Gamble Identification
- Take chances Analysis
- Gamble Mitigation Planning
- Risk Mitigation Programme Implementation
- Risk Tracking
Risk Management Program (RMP) Objectives
The goal of well-written RMP Objectives is to provide a repeatable process that reduces risk on a project or programme. The post-obit are a few objectives of a risk management plan that an system tin aim for.
Advertisements
- Reduce Schedule Impacts
- Reduce development price
- Increase organisation operation
- Ensure proper communication
- Determine run a risk priorities
Take a chance Management Process in the Risk Direction Plan (RMP)
The chance management procedure consists of 8 (8) steps and should exist detailed in the Take a chance Direction Programme.
- Step i: Document the Gamble Approach: The Program Manager (PM) and contractor shall document the approach for managing risk equally an integral part of the Systems Engineering Process.
- Step 2: Place and Document Risks:
Risks are identified through a systematic analysis process that includes arrangement hardware and software, system interfaces (to include human being interfaces), and the intended utilise of the application and operational surround. - Stride iii: Assess and Certificate Chance:
The severity category and a probability level of the potential mishap(s) for each risk across all organisation modes are assessed. - Footstep 4: Identify and Certificate Run a risk Mitigation Measures: Potential take a chance mitigation(due south) shall exist identified, and the expected gamble reduction(s) of the culling(s) shall be estimated and documented in the Chance Tracking System (HTS). The goal should ever be to eliminate the hazard if possible. When a hazard cannot be eliminated, the associated adventure should be reduced to the lowest adequate level inside the constraints of cost, schedule, and performance by applying the arrangement condom design order of precedence. The system rubber design gild of precedence identifies culling mitigation approaches and lists them in order of decreasing effectiveness.
- Step 5: Reduce Risk: Mitigation measures are selected and implemented to accomplish an adequate risk level. Consider and evaluate the cost, feasibility, and effectiveness of candidate mitigation methods as part of the Systems Applied science Process and Integrated Product Team (IPT) processes. Nowadays the current hazards, their associated severity and probability assessments, and status of chance reduction efforts at technical reviews.
- Step 6: Verify, Validate, and Certificate Risk Reduction: Verify the implementation and validate the effectiveness of all selected hazard mitigation measures through appropriate analysis, testing, demonstration, or inspection. Certificate the verification and validation in the HTS.
- Footstep 7: Accept Risk and Document: Before exposing people, equipment, or the environment to known system-related hazards, the risks shall be accustomed by the advisable authority as defined in DoDI 5000.02. The system configuration and associated documentation that supports the formal gamble credence determination shall be provided to the Government for memory through the life of the system.
- Pace 8: Manage Life-Wheel Adventure: Afterwards the system is fielded, the system program office uses the system rubber process to identify hazards and maintain the HTS throughout the arrangement's life-cycle. This life-cycle endeavour considers any changes to include, just not limited to, the interfaces, users, hardware and software, mishap data, mission(s) or contour(s), and system health data. Procedures shall be in place to ensure gamble management personnel are enlightened of these changes, e.1000., by being part of the configuration control process.
Risk Mitigation Strategies in the Risk Direction Plan (RMP)
Agreement Risk Mitigation in Stride iv of the Risk Direction Process is critical in developing an RMP. For each adventure that is identified, the blazon of mitigation strategy must be determined and the details of the mitigation described in the RMP. The intent of the risk mitigation plan is to ensure successful chance mitigation occurs. The well-nigh appropriate strategy is selected from these mitigation options:
Advertisements
- Risk Avoidance: This is when it'due south decided to perform other activities that don't behave the identified chance by eliminating the root cause and/or consequence. It seeks to reconfigure the project such that the risk in question disappears or is reduced to an adequate value.
- Risk Controlling: This is when you lot control the risk past managing the crusade and/or upshot. Risk command tin can take the form of installing data-gathering or early alert systems that provide information to assess more accurately the impact, likelihood, or timing of a run a risk. If a warning of risk can exist obtained early enough to take activity against it, then information gathering may be preferable to more tangible and possibly more than expensive actions.
- Risk Transfer/Sharing: This is when you share the risk with a third party like an insurance company or subcontractor.
- Take chances Assumption: Is accepting the loss, or benefit of proceeds, from a risk when it occurs. Risk assumption is a feasible strategy for small risks where the cost of insuring against the adventure would be greater over time than the total losses sustained.
Gamble Management Plan (RMP) Development Steps
An RMP should exist structured to identify, appraise, and mitigate risks that have an impact on overall program life-wheel cost, schedule, and/or performance. It should also ascertain the overall plan approach to capture and manage root causes. It should be created before and after you create the Integrated Master Schedule (IMS), as it will be looking at the tasks in the Projection Schedule and other factors for potential risk items.
10 Steps in Developing a Risk Management Plan (RMP)
- Footstep 1: Constitute the basic approach and working structure
- Step 2: Develop and document an overall hazard management process (See To a higher place)
- Stride 3: Establish the purpose and objective
- Step 4: Assign responsibilities for specific areas
- Step five: Draw the assessment/analysis process
- Step 6: Document sources of information
- Step 7: Listing potential chance and their impacts
- Step 8: Develop mitigation strategies
- Step 9: Establish reporting/tracking procedures
- Footstep 10: Write Program
Risk Management Programme (RMP) Format
The Risk direction plan should follow a standardized format from the organisation. An example RMP format: [ane]
- Introduction
- Programme Summary
- Risk Direction Strategy and Process
- Responsible/Executing Organization
- Hazard Management Process and Procedures
- Risk Identification
- Run a risk Cess Matrix
- Risk Analysis
- Take chances Mitigation Planning
- Risk Mitigation Implementation
- Risk Tracking
Template: Risk Management Plan
Template: Project Adventure Management
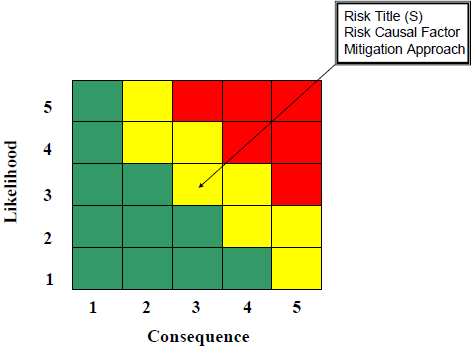
Use the Run a risk Reporting Matrix
The risk management programme should item how to use the Hazard Reporting Matrix is used to determine the level of risks identified within a program. The level of risk for each root cause is reported as
low (green)
,
moderate (xanthous)
, or
high (cherry-red)
. 
Writing a Good Risk Management Plan (RMP)
The cardinal to writing a skillful programme is to provide the necessary information so the program squad knows the goals, objectives, and the program office's chance management process. Although the program may be specific in some areas, such as the assignment of responsibilities for regime and contractor participants and definitions, it may exist full general in other areas to allow users to choose the nigh efficient manner to go on.
[i]
Run a risk Management Program (RMP) Updates
The Program Direction Part (PMO) should periodically review and update the RMP at major acquisition events. At the end of each Acquisition Phase, risk planning should be used in grooming for the side by side phase. [1]
Gamble Direction Program (RMP) in other Acquisition Documents
The plan is integral to overall program planning and should exist addressed in the program Acquisition Strategy, and/or the Systems Engineering science Programme (SEP).
[i]
AcqNotes Tutorial
AcqLinks and References:
- DoD Risk, Result, and Opportunity Management Guide for Defence force Acquisitions- Jan 2017
- (Old) DoD Risk Issue and Opportunity Management Guidance for Defense Acquisition Programs – June 2015
- [ane] DoD Chance Management Guidebook – Section 8 – Aug 06 (Outdated)
- Hazard Cess Checklist
- Chance Assessment Worksheet and Direction Programme
- Continuous Risk Direction Guidebook past Carnegie Melon
- Template: Run a risk Management Plan
- Template: Project Rick Management Template
Updated: 12/29/2021
Rank: G10
Source: https://en.asriportal.com/51283/what-rm-process-step-requires-a-cycle-of-continuous-reassessment/
0 Response to "What Rm Process Step Requires a Cycle of Continuous Reassessment"
Postar um comentário